Study Objective
Delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS) is a circadian-rhythm sleep disorder characterized by abnormally late sleep and wake times. Melatonin, taken in the evening, advances sleep and circadian phase in patients with DSPS. However, little is known about the most effective dose or time of administration. In the present study, we tested the effectiveness of melatonin to advance the timing of sleep and circadian phase in individuals with DSPS.
Design
Following baseline assessment of sleep and circadian phase, subjects were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 treatment groups. The administration of melatonin (0.3 or 3.0 mg) or placebo was double-blinded.
Setting
All procedures were conducted on an outpatient basis.
Participants
Thirteen subjects with DSPS, recruited via flyers, advertisements, and referrals from the Sleep Clinic, completed this study.
Interventions
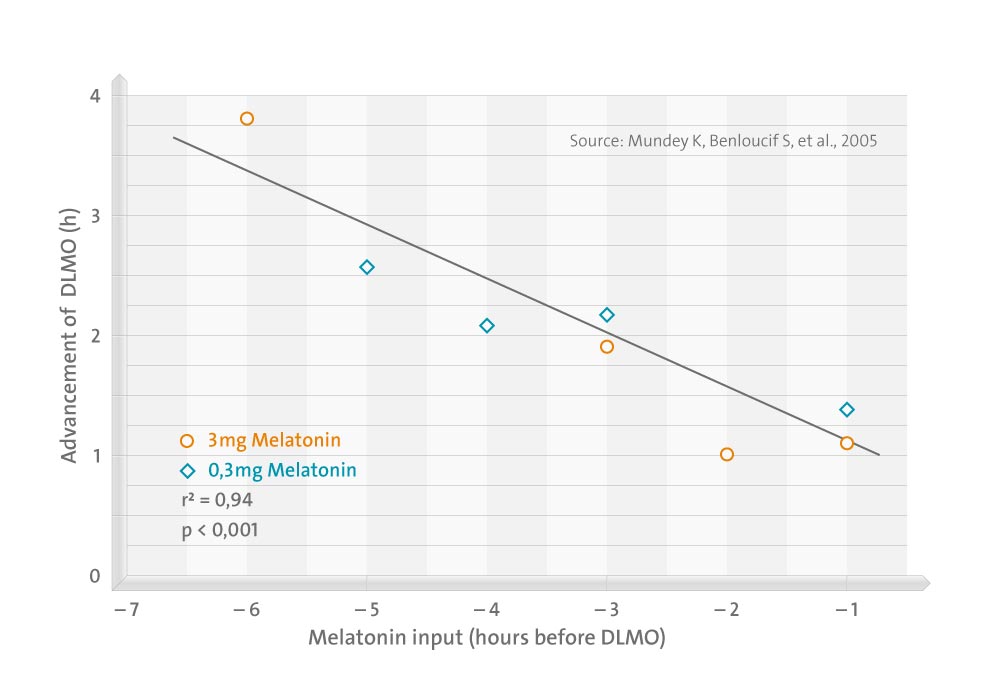
Melatonin (0.3 or 3.0 mg) or placebo was administered between 1.5 and 6.5 hours prior to dim light melatonin onset for a 4-week period.
Measurements and Results
Both doses of melatonin advanced the circadian phase of endogenous melatonin. The magnitude of phase advance in dim-light melatonin onset correlated strongly with the time of melatonin administration, with earlier times being more effective (r2 = 0.94, P < .0001). Similar, though weaker, relationships were obtained between the timing of melatonin administration and changes in sleep time.
Conclusions
These results indicate that melatonin advances the circadian clock and sleep in patients with DSPS in a phase-dependent manner. This is the first study that reports a relationship between timing of melatonin administration and phase changes in patients with DSPS.