Basic Facts
Medical Studies on Melatonin – Basic Facts

Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is mainly produced in the pineal gland, located in the brain – especially during the night in complete darkness. This is when the melatonin level rises to eight times of the level during the day. This signals to the organism that it is time for the organs and bodily functions to rest, but also to initiate vital repair mechanisms. This makes melatonin the most important internal timer.
Disruptions to cycles caused by light
On the other hand, even the slightest flash of light can affect this critical process, especially the blue light from TVs and smartphones, the light from an alarm clock or street lighting. These everyday appliances have proven to be highly disruptive to our internal cycles and have a substantially adverse impact on our melatonin balance.
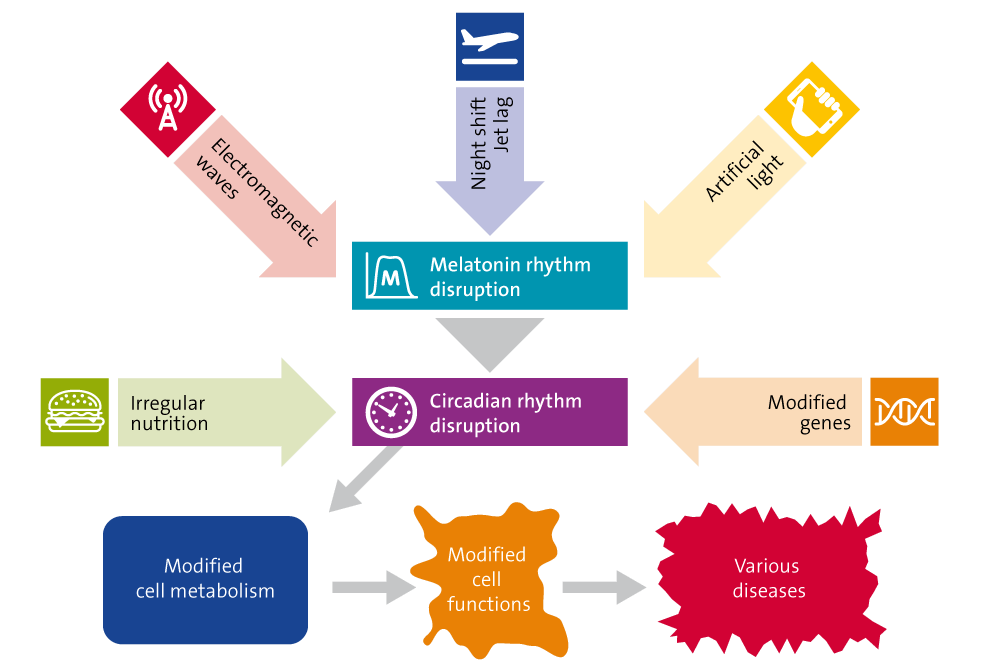
Melatonin keeps our internal clock ticking
Each flash of light passes through the retina to reach the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which is connected to the pineal gland and serves as a control centre and “master clock” for the brain. Melatonin provides the timing for this internal clock, not only letting the brain know that it should switch to “night mode”, but also passing this information on to every other organ and cell in the body. If this natural mechanism is disrupted by light during the night, this has serious consequences not only for the day/night cycle, but also for the function of the organs and the development and course of many diseases.
Every cell contains melatonin
Only recently did it become known that the “powerhouses” of each cell, the mitochondria, are also capable of producing melatonin. This melatonin is not passed into the blood, but rather is used to regulate certain functions in each of the cells. This production is also partly controlled by the melatonin in the pineal gland, meaning that disorders of the pineal gland can also result in changes in how these cells function, which may result in organ damage, for example.
Medical Studies on Melatonin – Basic Facts
Biological correlates of altered circadian rhythms, autonomic functions and sleep problems in autism spectrum disorder
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a complex and multifaceted neurobehavioral syndrome. In the last decades, several studies highlighted an increased prevalence of sleep problems in ASD, which would be associated with autonomic system and circadian rhythm disruption.
Melatonin ameliorates tau-related pathology via the miR-504-3p and CDK5 axis in Alzheimer’s disease
Intracellular accumulation of the microtubule-associated protein tau and its hyperphosphorylated forms is a key neuropathological feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Melatonin has been shown to prevent tau hyperphosphorylation in cellular and animal models. However, the molecular mechanisms by which melatonin attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation and tau-related pathologies are not fully understood.
Melatonin Potentiates Exercise-Induced Increases in Skeletal Muscle PGC-1α and Optimizes Glycogen Replenishment
Compelling evidence has demonstrated the effect of melatonin on exhaustive exercise tolerance and its modulatory role in muscle energy substrates at the end of exercise. In line with this, PGC-1α and NRF-1 also seem to act on physical exercise tolerance and metabolic recovery after exercise.
Melatonin, macrophages and microbiota: Interactions
This commentary summarizes and highlights the recent research reports of the group headed by Professor Wenkai Ren. Their research has been focused in two important investigative areas, namely, the role of melatonin in the regulation of macrophage polarization and the functional implications of melatonin for the gastrointestinal microbiota. Both these subjects are of high interest to melatonin biologists since both have significant implications in clinical and veterinary medicine.
The bacteriostatic property of melatonin targets peptic ulcer disease and cholangiocarcinoma
The marked drop in the frequency of Helicobacter pylori infection resulting from the use of antibiotics and potent anti-acid medications has substantially lowered the prevalence of peptic ulcer disease in recent decades.
Accuracy and precision of 31P-MRS assessment for evaluating the effect of melatonin-pretreated mitochondria transferring on liver fibrosis of rats
This study examined the reliability of 31phosphorus-magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31P-MRS) to measure parameters of liver metabolic function in the intact animals. These parameters can help us to evaluate the severity and prognosis of liver fibrosis.
SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses negatively influence mitochondrial quality control: beneficial effects of melatonin
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are a group of single stranded RNA viruses, of which some of them such as SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 are associated with deadly worldwide human diseases. Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), a condition caused by SARS-CoV-2, results in acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) associated with high mortality in the elderly and in people with underlying comorbidities.
Role of melatonin in the angiogenesis potential; highlights on the cardiovascular disease
Melatonin possesses multi-organ and pleiotropic effects with potency to control angiogenesis at both molecular and cellular levels. To date, many efforts have been made to control and regulate the dynamic of angiogenesis modulators in a different milieu.
Melatonin: From Pharmacokinetics to Clinical Use in Autism Spectrum Disorder
The role of melatonin has been extensively investigated in pathophysiological conditions, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Reduced melatonin secretion has been reported in ASD and led to many clinical trials using immediate-release and prolonged-release oral formulations of melatonin. However, melatonin’s effects in ASD and the choice of formulation type require further study.
Melatonin: Effects on Cartilage Homeostasis and Therapeutic Prospects in Cartilage-related Diseases
Cartilage is a relatively simple connective tissue that plays a variety of roles in the human body, including joint support and protection, load bearing of the intervertebral discs, joint lubrication, formation of the external structure of the ears and nose and support of the trachea. The maintenance of cartilage homeostasis is therefore crucial. Cartilage-related diseases are difficult to diagnose and treat because their molecular and pathological mechanisms are not fully understood.
Evening home lighting adversely impacts the circadian system and sleep
The regular rise and fall of the sun resulted in the development of 24-h rhythms in virtually all organisms. In an evolutionary heartbeat, humans have taken control of their light environment with electric light. Humans are highly sensitive to light, yet most people now use light until bedtime. We evaluated the impact of modern home lighting environments in relation to sleep and individual-level light sensitivity using a new wearable spectrophotometer.
Can Melatonin Be a Potential “Silver Bullet” in Treating COVID-19 Patients?
The therapeutic potential of melatonin as a chronobiotic cytoprotective agent to counteract the consequences of COVID-19 infections has been advocated. Because of its wide-ranging effects as an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory compound, melatonin could be unique in impairing the consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The role of melatonin in colorectal cancer treatment: a comprehensive review
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, known as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths annually.
Chronotype, circadian rhythms and mood.
Growing evidence shows a link between mood and chronotype. The majority of studies measure chronotype as a preference for morning/evening activities, rather than actual sleep behaviour (i.e. midsleep) or biological markers of sleep timing (e.g. dim light melatonin onset).
Melatonin Synthesis and Function: Evolutionary History in Animals and Plants.
Melatonin is an ancient molecule that can be traced back to the origin of life. Melatonin's initial function was likely that as a free radical scavenger. Melatonin presumably evolved in bacteria; it has been measured in both α-proteobacteria and in photosynthetic cyanobacteria.
Virtual discovery of melatonin receptor ligands to modulate circadian rhythms.
The neuromodulator melatonin synchronizes circadian rhythms and related physiological functions via actions at two G protein-coupled receptors: MT1 and MT2.
Melatonin in the treatment of fibromyalgia symptoms: A systematic review.
The available pharmacological modalities for the treatment of fibromyalgia (FM) are associated with a variety of adverse effects and limited benefits. In this study, we systematically reviewed the impact of melatonin in the treatment of FM.
The association between sleep chronotype and obesity among black and white participants of the Bogalusa Heart Study.
Research indicates that sleep duration and quality are inter-related factors that contribute to obesity, but few studies have focused on sleep chronotype, representing an individual's circadian proclivity, nor assessed these factors in racially diverse middle-aged samples.
Melatonin inhibits GABAergic neurons in the hypothalamus consistent with a reduction in wakefulness.
Although melatonin is necessary for circadian regulation of sleep, the mechanisms underlying this effect of melatonin are still unclear. In the present study, we showed that melatonin suppressed the activity of GABAergic neurons in the lateral hypothalamus, which has been reported to play a crucial role in maintaining wakefulness.
Effects of light on human circadian rhythms, sleep and mood.
Humans live in a 24-hour environment, in which light and darkness follow a diurnal pattern. Our circadian pacemaker, the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) in the hypothalamus, is entrained to the 24-hour solar day via a pathway from the retina and synchronises our internal biological rhythms.
Melatonin: Countering Chaotic Time Cues.
Last year melatonin was 60 years old, or at least its discovery was 60 years ago. The molecule itself may well be almost as old as life itself. So it is time to take yet another perspective on our understanding of its functions, effects and clinical uses.
New Insights Into the Circadian Rhythm and Its Related Diseases.
Circadian rhythms (CR) are a series of endogenous autonomous oscillators generated by the molecular circadian clock which acting on coordinating internal time with the external environment in a 24-h daily cycle.
Melatonin MT1 receptor as a novel target in neuropsychopharmacology: MT1 ligands, pathophysiological and therapeutic implications, and perspectives.
Melatonin (MLT), a neuromodulator mainly acting through two G-protein coupled receptors MT1 and MT2, regulates many brain functions, including circadian rhythms, mood, pain and sleep. MLT and non-selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonists are clinically used in neuropsychiatric and/or sleep disorders.
Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers.
Melatonin is uncommonly effective in reducing oxidative stress under a remarkably large number of circumstances. It achieves this action via a variety of means: direct detoxification of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species and indirectly by stimulating antioxidant enzymes while suppressing the activity of pro-oxidant enzymes.
Melatonin, the Hormone of Darkness: From Sleep Promotion to Ebola Treatment.
Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the enigmatic pineal gland in response to darkness, hence the name hormone of darkness. It has generated a great deal of interest as a therapeutic modality for various diseases particularly sleep disorders.
Beneficial actions of melatonin in the management of viral infections: a new use for this “molecular handyman”?
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a multifunctional signaling molecule that has a variety of important functions. Numerous clinical trials have examined the therapeutic usefulness of melatonin in different fields of medicine.
Clinical uses of melatonin: evaluation of human trials.
During the last 20 years, numerous clinical trials have examined the therapeutic usefulness of melatonin in different fields of medicine. The objective of this article is to review, in depth, the science regarding clinical trials performed to date.
Melatonin: a multitasking molecule.
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) has revealed itself as an ubiquitously distributed and functionally diverse molecule. The mechanisms that control its synthesis within the pineal gland have been well characterized and the retinal and biological clock processes that modulate the circadian production of melatonin in the pineal gland are rapidly being unravelled.
Melatonin: a pleiotropic molecule regulating inflammation.
Melatonin is a neurohormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates sleep and circadian functions. Melatonin also regulates inflammatory and immune processes acting as both an activator and inhibitor of these responses.
Melatonin: action as antioxidant and potential applications in human disease and aging.
This review aims at describing the beneficial properties of melatonin related to its antioxidant effects. Oxidative stress, i.e., an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defences, is involved in several pathological conditions such as cardiovascular or neurological disease, and in aging. Therefore, research for antioxidants has developed. However, classical antioxidants often failed to exhibit beneficial effects, especially in metabolic diseases.
Melatonin signaling and cell protection function.
Besides its well-known regulatory role on circadian rhythm, the pineal gland hormone melatonin has other biological functions and a distinct metabolism in various cell types and peripheral tissues. In different tissues and organs, melatonin has been described to act as a paracrine and also as an intracrine and autocrine agent with overall homeostatic functions and pleiotropic effects that include cell protection and prosurvival factor.
Melatonin, synthetic analogs, and the sleep/wake rhythm.
Melatonin, a widespread hormone in the animal kingdom, is produced by several organs and tissues besides the pineal gland. Whilst extrapineal melatonin behaves as a cytoprotective molecule, the pineal produces the hormone in a rhythmic manner. The discovery of melatonin in 1958, and the characterization of its synthesis somewhat later, let to the description of its photoperiodic regulation and its relationship with the biological rhythms such as the sleep/wake rhythm.
Randomized, double-blind clinical trial, controlled with placebo, of the toxicology of chronic melatonin treatment.
The objective of the present study was to assess the toxicology of melatonin (10 mg), administered for 28 days to 40 volunteers randomly assigned to groups receiving either melatonin (N = 30) or placebo (N = 10) in a double-blind fashion.