The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of oral melatonin supplementation on oocyte and embryo quality in patients in an assisted reproductive technologies program.
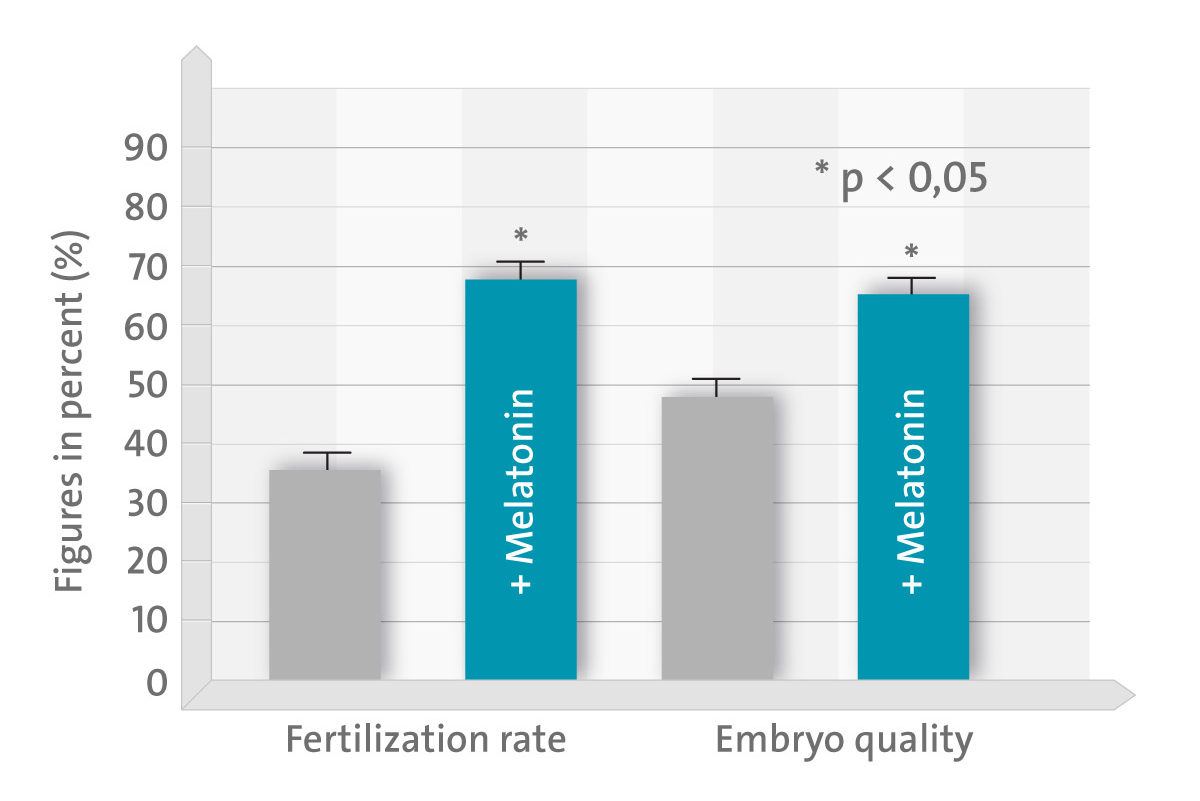
All patients were treated for at least 2 weeks with melatonin (3 mg/day). To evaluate the cumulative effect of melatonin supplementation, we compared cycle outcomes between the first (no supplementation) and second cycles (melatonin supplementation) of patients who completed two treatment cycles. There were no significant differences in maturation rates (p = 0.50), blastocyst rates (p = 0.75), and the rate of good quality blastocysts (p = 0.59) between the first and second cycles. The fertilization rate of ICSI was higher in the second cycle than that in the first cycle (69.3 versus 77.5%). Being limited to patients with a low fertilization rate in the first cycle (<60%), the fertilization rate dramatically increased after melatonin treatment (35.1 versus 68.2%). The rate of good quality embryos also increased (48.0 versus 65.6%).
An important finding in our study was that oral melatonin supplementation can have a beneficial effect on the improvement of fertilization and embryo quality and this may have occurred due to a reduction in oxidative damage.